Categories
Latest blog
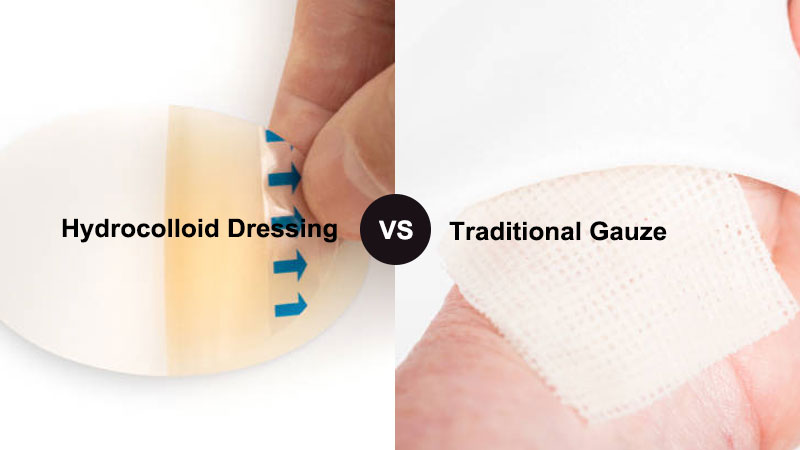
Selecting an appropriate wound dressing is an important aspect of wound management. Among the most commonly used options are hydrocolloid dressings and traditional gauze, each offering distinct characteristics and use considerations.
This article provides an educational comparison of hydrocolloid dressings and traditional gauze, highlighting their key differences to support informed decision-making within professional wound care practices.
A hydrocolloid dressing is an advanced wound dressing composed of hydrophilic particles—such as gelatin or carboxymethylcellulose—combined with an adhesive backing. When in contact with wound moisture, the dressing absorbs exudate and forms a gel-like layer.
Hydrocolloid dressings are commonly used in professional wound care products portfolios due to their ability to maintain a moist wound environment and provide a protective barrier over the wound surface.
Traditional gauze is a widely used wound dressing material made from woven or non-woven fabric. It is commonly applied to cover wounds, absorb exudate, or protect the wound area during short-term care.
Gauze dressings are frequently used in healthcare settings because of their simplicity, availability, and adaptability across a wide range of wound types.
The primary differences between hydrocolloid dressings and traditional gauze relate to moisture management, wear time, wound protection, and monitoring needs.
Hydrocolloid dressings are designed to interact with wound moisture, helping maintain a moist environment. Traditional gauze, by contrast, typically absorbs moisture and may allow the wound to dry if not changed regularly.
Hydrocolloid dressings are often associated with longer wear times, depending on wound condition. Gauze dressings usually require more frequent changes, especially when exudate is present.
Hydrocolloid dressings provide a barrier that can help shield the wound from external contaminants. Gauze offers basic coverage but may require secondary dressings for additional protection.
Gauze allows for frequent wound inspection due to its ease of removal. Hydrocolloid dressings may limit direct visibility while in place, making regular assessment protocols important.
| Feature | Hydrocolloid Dressing | Traditional Gauze |
|---|---|---|
| Dressing type | Advanced wound dressing | Basic wound dressing |
| Moisture interaction | Forms gel with wound exudate | Absorbs moisture |
| Wound environment | Helps maintain moisture | May allow drying |
| Typical wear time | Longer wear time possible | Requires frequent changes |
| Protection level | Occlusive or semi-occlusive | Minimal without secondary dressing |
| Wound visibility | Limited while in place | Easy to inspect |
| Common care settings | Hospitals, clinics, home care | Hospitals, clinics, first aid |
Hydrocolloid dressings are commonly used for superficial or partial-thickness wounds, early-stage pressure injuries, closed surgical wounds, and friction-related skin injuries, depending on professional assessment and care protocols.
Traditional gauze is widely used for wounds requiring frequent inspection, initial wound coverage, or short-term management. It is also commonly used as a secondary dressing in combination with other wound care materials.
The selection between hydrocolloid dressings and traditional gauze depends on several factors, including:
Wound depth and size
Exudate level
Frequency of wound monitoring
Care environment
Compatibility with other wound care products
Understanding these differences supports clearer communication and more informed selection within professional wound care settings.
Hydrocolloid dressings and traditional gauze each play an important role in wound care. Hydrocolloid dressings are commonly associated with moisture management and extended wear, while gauze remains a versatile and widely used option for basic wound coverage and frequent assessment.
Rather than serving as alternatives in all cases, these dressing types are often used as part of a broader wound care system, allowing healthcare professionals to select appropriate materials based on wound characteristics and care requirements.
Learn more about our range of hydrocolloid dressings and professional wound care products designed for clinical and care environments.
Hydrocolloid dressings and gauze are used for different purposes. Selection depends on wound type, moisture level, monitoring needs, and care setting. Neither option is universally better; both are commonly used within professional wound care practices.
Gauze is often preferred when frequent wound inspection is required, when wounds produce high levels of exudate, or during short-term wound management. It is also commonly used as a secondary dressing alongside other wound care materials.